CRUDE OIL
INTRODUCTION:
FOSSIL FUEL:
Fossils are generally the remains or impressions of prehistoric living beings left over embedded in rocks and
preserved in a petrified(synonymous to ossified and in terms of a fossil, it means that it changed into a stony substance) form.
Fossil fuel is similar to a fossil. Fossil fuel releases heat and energy upon combustion. The major difference between fossils and fossil fuels lies in their formation. Generally, in a fossil, you can see the petrified form of an organism embedded in rocks, while in a fossil fuel you cannot. Fossil fuels are formed over millions of years as dead organisms are subjected to extreme heat and pressure(as it is formed deep under the layers of the crust). Living beings constitute compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen as the major components (hydrocarbons). So, the combustion of these compounds releases heat and water. During the formation of fossil fuels, organic matter is subjected to extreme heat and pressure to become compressed and compact. They undergo several chemical changes and form combustible substances. In the formation of fossil fuels, we can observe the formation of three major substances, namely, COAL, PETROLEUM and NATURAL GAS.
Fossil fuels constitute
CRUDE OIL:
Crude oil is obtained by Oil Drilling. It is nothing but boring into Earth and recovering oil.
source: Wikipedia. A typical oil drill.
Now, where should I drill to obtain oil?
Here we have to follow a few steps to find out the answer. These steps include:
- studying the Structural Geology of the place.
- Structural geology is a subdiscipline of geology that studies how rocks deform in response to the stresses that act within the Earth.
- Sedimentary Basin Analysis
- Sedimentary basins are regions of the Earth where long-term subsidence(Subsidence is the sudden sinking or gradual downward settling of the ground's surface with little or no horizontal motion) creates accommodation space for the accumulation of sediments. As the sediments are buried, they are subjected to increasing pressure that kick starts the processes of compaction and lithification that transform them into sedimentary rock.
- Reservoir Characterisation
- After the above analysis, if we discover a crude oil reserve, we have to check if the quality and composition of the crude oil is feasible and profitable.
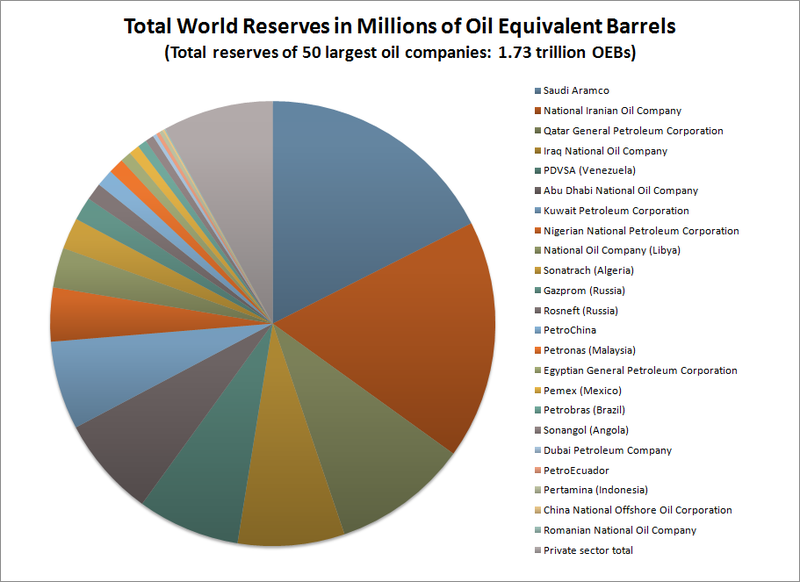
Image credits: Wikipedia. Oil Reserves around the globe
Crude oil is generally filled and transported in Barrels.
Barrels:
Crude oil consumption, as per an estimate, is 100 million Barrels per Day.
CLASSIFICATION:
- Its API gravity(American Petroleum Institute) gravity with a reference point 10.
- Click here for API gravity Formulae. In simple terms, it's the inverse of specific gravity.
- API gravity provides more convenience to find the quality of petrol when compared with specific gravity. A higher value of API gravity indicates higher quality petroleum. As Specific gravity is less than 1(at 277K) for Fluids lighter than water(petroleum) its values are in decimals. the lower the value of specific gravity the higher is the quality of petroleum.
- If API gravity is more than 10, petroleum is lighter than water (and has more demand) as it contains a large amount of gasoline(petrol).
- If API gravity is less than 10, petroleum is heavier than water(as it contains impurities).
- The amount of sulphur as a constituent:
- Petroleum with more sulphur content is sour and has less demand in the market. As sulphur emits sulphur oxides which are harmful to the environment, it does not meet the standards of petroleum set by the countries in which the petroleum is sold.
- Petroleum with less sulphur content is sweet and has high demand in the market.
- The pricing reference of Petroleum in the market:
- This classification is based on the above two classifications combined.
COMPOSITION:
Crude oil's major constituents are saturated hydrocarbons, cyclic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons and organic compounds(constituting nitrogen, sulphur, oxygen). Crude oil reserves also contain trace amounts of iron, nickel, copper and vanadium.
The alkanes with a long parent chain(solids) are craked and converted into alkanes with a small parent chain(gases and liquids). Gaseous and liquid hydrocarbons are used as fuel. (Description: The number of carbons in the parent chain of alkanes influences the state of the compound. The longer the parent chain, the higher the mass and melting point. So, alkanes with longer parent chains are solids while those with shorter parent chains are fluids.










0 Comments