Donating one's body after death is the highest form of social service — even in death, the body becomes a teacher, a healer, and a light for the living.
After death, one can donate their body — Cadaver donation — to medical institutions for advancement of medical sciences or donate organs and tissues for transplantation to the recipients.
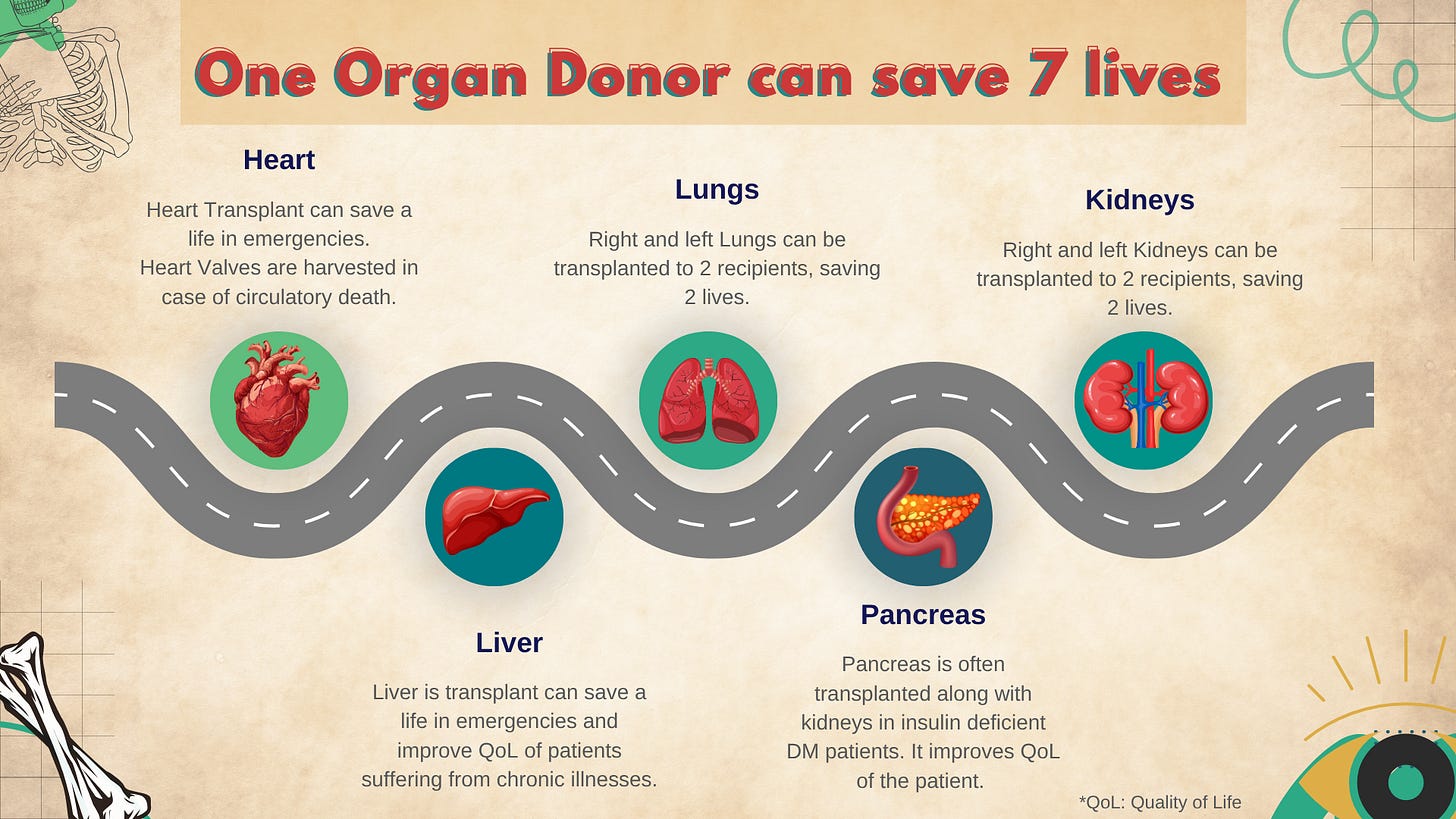
The phrase “Organ Donation” includes both organs(like kidneys, liver, heart) and tissues(like skin, cornea, heart valves, bones and tendons).
I was stunned by looking at the number of live organ donations in India. Deceased organ donation transplants are only 16% while live organ donation transplants account for 84 % of total organ transplants in India in the year 2023 according to data published by NOTTO MoHFW reports. (3) Most of the patients hesitate to even register as a recipient as there is no guarantee one would receive an organ — unless a live donor is willing to donate their kidney or a part of their liver. Average waiting time for a deceased kidney in India is over 2–3 years in major centres. (7)
Why people hesitate to become an organ donor in India? Here’s my experience overcoming the hesitation and finally making the choice to get registered as an organ donor.
Introduction to Death - Are we a Brain with a Body (or) a Body with a Brain?
Discussions about death can be scientific or philosophical. In our article lets focus on scientific arguments(low-key this sentence is inspired from NCERT biology textbook).
In medical terms, a human can be certified dead on the basis of brain death or circulatory death. Terms like clinical death and biological death are also defined in clinical setting.
A lay-man would say a person is dead if that person is no longer breathing or that person’s heart beat can’t be heard anymore. This notion is aligned with circulatory death criteria.
Are we a brain with a body (or) a body with a brain? This is a paradoxical question. A person can die if their vital organs(like kidneys, liver, heart) are failing while their brain might still be functional and also if every other organ is functioning while brain is not.
In the first scenario, patient dies of multiple organ failure where the primary reason for death doesn’t lie with the brain. It’s the failing organs that cannot keep the body alive.
In second case, when brain loses it’s function, lungs can no longer perform breathing(respiratory centre is located in brain) — leading to hypoxia and multiple organ failure. In this case, the point of loss of brain’s function marks the time of death. Brain dead patients are supported by ventilators as a measure of management of patients before organ donation operation to save organs from ischemic injury to organs. Even if patient is registered as an organ donor, family’s consent is taken before organ donation operation in almost every country.
Medically death can be classified into Brain death, Circulatory death, Clinical death and Biological death. This classification underlines the cause of death, more like what organs of the body failed leading to death. When you are looking at legal and criminal aspects you would be looking at how the person died, like the mode of death.
Clinical Death
If you are familiar with CPR, it is known that one can mostly restart anyone’s heart if a person goes into sudden cardiac arrest by timely performing the CPR. Even if CPR cannot bring back pulse, there is a window period of about 5 minutes(the maximum recorded time is beyond 10 minutes, but 5 minutes is considered standard) for spontaneous return of pulse after performing CPR. This phenomenon of spontaneous autoresuscitation after cessation of CPR is known as Lazarus phenomenon. Lazarus phenomenon is real but rare (<1% of CPR cases). This is why time of death due to circulatory death is declared 5 minutes after cessation of CPR .In case of DNR(do not resuscitate) patients the time of death is declared at the time of cardiac arrest. DNRs are not yet legally streamlined and widely accepted in India, though it is part of some hospital policies and palliative care plans. The 2018 Supreme Court ruling allows passive euthanasia and advance directives, but DNR implementation is inconsistent. (6) This case where the person can be brought back to life with CPR after temporary cessation of heart beat and breathing is considered as clinical death.
Biological death
Biological death often follows clinical death when resuscitation efforts fail. Biological death can be viewed as multiple organ failure including brain. Biological death is the final dead end. A point of no return and no virtual signs of life (this refers to brain dead patients on ventilators who seem to be alive but in reality are dead).
Brain Death
Brain death occurs due to irreversible cessation of all functions of entire brain including brainstem. (1)
Brain death does not always imply circulatory death as cardiac function(autonomous organ) is often preserved in brain dead patients. In advanced ICUs — supported by mechanical ventilators — the damage to the remaining organs due to hypoxia can be minimized. (8)
Brain death is a sensitive topic as brain dead patients virtually look like they are breathing. Virtually because the ventilators only move air like a pump to simulate breathing with calculated rhythmic inflow and outflow of air into the lungs. The patient’s neurologic function is lost and they cannot breathe independently. This happens as the activity of respiratory centre in brainstem is lost and there is no actual neurological respiration. This virtual breathing is the reason why brain death is not accepted as absolute death by everyone due to cultural, moral and religious reasons. Circulatory death is widely accepted by everyone as it’s inline with the lay-man’s definition of death. Most families do not accept brain death due to various reasons. Some of these reasons include ethical and moral concerns as the patients are virtually breathing. Some religions like Shinto in Japan do not accept brain death and this reflects their statistical data as more than 80% of organ donations happen after circulatory death.
Even though the patient supported by ventilator appears to be virtually breathing, the patient is dead. All the brain death certified patients after undergoing brain death testing — 100% of them — never regained consciousness even when they were supported by life support machinery until they died from other causes. The reason is — the brain is no longer functional and eventually undergoes progressive liquefactive necrosis, meaning brain tissue dies due to absence of blood supply and oxygen.
The time of completion of brain death testing is considered as the time of death of the patient. Brain death testing is a series of tests performed on patients suspected to be brain dead. To suspect someone to be brain dead, there is a pre-requisite criteria to be followed even before starting brain death testing. Some countries stipulate specific rules and specific qualifications of doctors and number of doctors that are needed to evaluate and certify brain death.
Pre-requisites required to proceed with brain death testing:
The patient should be in irreversible coma state and the cause must be known. It is mandatory to rule out all the metabolic causes and drug effects that might influence patient’s coma state. The patient must be normothermic, and have normal blood pressure.
Rule out vegetative state, persistent vegetative state and locked-in syndrome.
How brain death is evaluated?
In India, brain death must be certified by a panel of four doctors, including the treating physician, neurologist/neurosurgeon, medical administrator, and an independent doctor, as per THOA rules.
This ensures the clinical treating team does not compromise the quality of care the patient receives.
Firstly, patient is checked for responsiveness. Then brain death testing is done, which includes various tests to check for brain stem reflexes(mainly mid-brain). Lets not go into the technicalities of this testing but eventually it all comes down to testing if patient is able to breath on their own confirming if the brainstem is functional or not. If any one of the reflexes is positive during the testing, the test should be aborted as the patient is alive.
In India brain death is legally accepted cause of death.
Circulatory death
Circulatory death, also known as cardiopulmonary death or death due to circulatory criteria, occurs due to irreversible cessation of cardiac and respiratory functions. (1)
Circulatory death aligns with lay-man’s definition of death unlike brain death.
In some cases, if brain death is not accepted by law or culturally by patient’s family, the life support machines are withdrawn and circulatory death follows. This measure deprives the oxygen in the body and stops heart beat. This measure compromises patient’s management after brain death for organ and tissue harvest operation as organs suffer damage due to ischemia and heart cannot be transplanted.
Controlled and Uncontrolled DCD
Donation after Circulatory Death(DCD) decisions are influenced by whether the cause of circulatory death is controlled or uncontrolled. Modified Maastricht classification of DCD classifies controlled and uncontrolled DCDs. (2)
In emergency cases when the patient is brought dead to the hospital or patient died due to unsuccessful resuscitation, the death is considered to be uncontrolled death as there was no chance of medical intervention. (2) In this case, only tissue donation can be feasible while organ donation cannot be feasible as organs would eventually suffer damage from ischemia.
DCD often follows Controlled Circulatory death. (2) Controlled death happens when non-beneficial treatment is withdrawn or patient goes into cardiac arrest in the ICU. In cases of organ donor registered patients, the treatment is withdrawn in operation theatre while providing drugs(morphine) to alleviate pain. There are no rules under THOA act, but in countries like UK and Canada, if patient doesn’t go into cardiac arrest within 1 hour of withdrawal of treatment, the patient is shifted to palliative care ward and organ donation is aborted.
Conclusion
To sum up death is
Irreversible cessation of entire brain function including brainstem and/or
Irreversible cessation cardiopulmonary functions
Now we are familiar with the concept of death. Lets move on to discuss the Technicalities and Ethical Concerns related to Organ Donation in coming up articles of this 3 article series, “Why it took me a month to get registered as a Deceased Organ Donor?”
AI Disclosure
This article series is the original work of the author. AI tools such as ChatGPT were used only to identify and correct factual inaccuracies.
Postscript
This article is for educational purpose only. This is an effort to raise awareness about organ donation and the potential of 1 organ donation in saving 7 lives and improving quality of life of many more. Do not take this decision impulsively. Discuss about organ donation with your family and friends before registering yourself as an organ donor.
If you needed an organ transplant would you have one? If so, please help others.
Register as an organ donor here https://notto.abdm.gov.in/register
References and Resources
Uniform Determination of Death Act (1981, USA) | UniformLaws.org
Modified Maastricht classification of DCD | ScienceDirect
Data of Organ Donation and Transplantation 2013-2023 | MohfwReport
Organ Donation: from Death to Life | Coursera
Timeline of perception of death | DeekshithVodelaSubstack
Supreme Court simplifies procedure to withhold life support of a terminally ill patient; Modifies guidelines given in 2018 Euthanasia Judgment | SCConline
The Current Scenario Of Kidney Transplants In India | NarayanaHealth.org
Management of the brain dead organ donor in the operation theatre (OT) | MoHFW


0 Comments